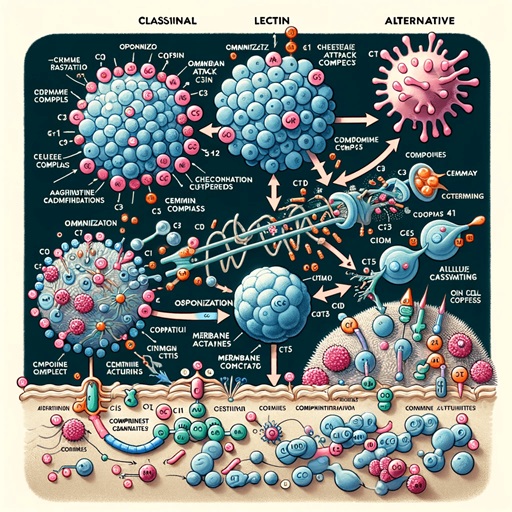
The complement system is a sophisticated part of the immune system that enhances the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells, promotes inflammation, and attacks the pathogen's cell membrane. This system is named for its capacity to "complement" the killing of pathogens by antibodies.
Comprising over 30 small proteins produced by the liver, the complement system circulates in the blood serum and within tissues throughout the body. These proteins are normally inactive but become sequentially activated in response to a pathogen. Activation can occur via three pathways: the classical pathway, which is triggered by antibodies bound to a pathogen; the lectin pathway, which is activated by mannose-binding lectin attaching to the pathogen surface; and the alternative pathway, which can be initiated directly by pathogen surfaces.
Each pathway leads to the cleavage of the protein C3, generating C3a and C3b fragments. C3b binds to the pathogen surface and can lead to direct opsonization—tagging the pathogen for destruction by phagocytes. C3a, along with other small fragments released during complement activation, acts as a chemoattractant to recruit immune cells to the site of infection and promote inflammation.
The final common step of the complement activation pathways is the assembly of the membrane attack complex (MAC). This complex forms a pore in the membrane of the target cell, leading to cell lysis and death. The MAC is particularly effective against gram-negative bacteria.
Regulation of the complement system is crucial, as overactivation can damage host cells. Regulators are present in blood plasma and on cell surfaces, ensuring the system is directed only at pathogens or damaged cells.
The complement system plays a crucial role not only in innate immunity but also as a bridge to adaptive immunity. It assists in clearing immune complexes and apoptotic cells, and in enhancing the humoral response and immune memory.
Understanding and manipulating the complement system has therapeutic potential for numerous diseases, including those that involve excessive or inappropriate activation of the complement pathways.