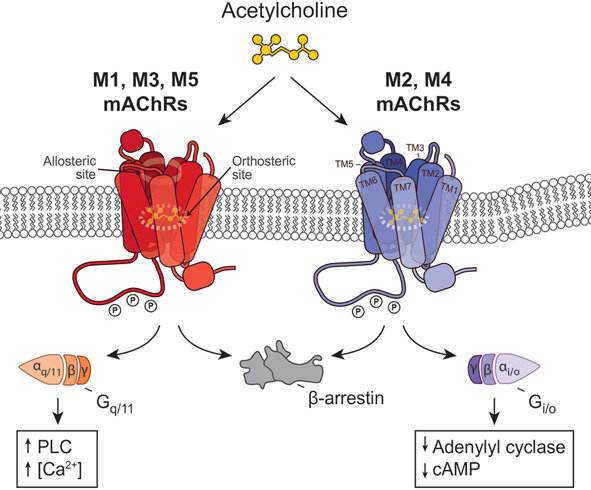
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) are a class of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) found in the central and peripheral nervous systems, as well as in various other tissues and organs throughout the body. These receptors are named after muscarine, a natural alkaloid compound found in certain mushrooms, which was one of the first substances discovered to activate them.
There are five subtypes of muscarinic receptors, designated as M1 through M5, each with distinct tissue distribution and functions. Here's an overview of their roles:
- M1 Receptors: Predominantly found in the central nervous system, particularly in regions associated with cognitive functions. Activation of M1 receptors is linked to memory and learning.
- M2 Receptors: Found in the heart, where they play a crucial role in regulating heart rate and cardiac contractility. Activation of M2 receptors slows heart rate and reduces the force of cardiac contractions.
- M3 Receptors: Present in smooth muscle tissues, such as those in the gastrointestinal tract, urinary bladder, and bronchial airways. Activation of M3 receptors leads to smooth muscle contraction.
- M4 Receptors: Distributed mainly in the central nervous system and involved in modulating neurotransmitter release. Their role in cognition and neuropsychiatric disorders is of interest.
- M5 Receptors: Located in certain areas of the brain and implicated in the modulation of dopamine release. Research suggests they may be relevant to Parkinson's disease and addiction.
Muscarinic receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and play a vital role in regulating a wide range of physiological processes, including heart rate, smooth muscle contraction, glandular secretion, and neurotransmitter release. They are targets for various drugs, including anticholinergic agents, which block their activity, and drugs used to treat conditions like bradycardia and neurodegenerative disorders.
Understanding the functions and regulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors is essential for developing therapies that modulate their activity and for advancing our knowledge of how they contribute to various physiological and pathological processes in the body.