-
Aromatase inhibitor
Anastrozole 是一种第三代非甾体选择性芳香化酶抑制剂。与其他芳香化酶抑制剂相比,它可能提供更高的选择性,没有任何固有的内分泌效应,并且对肾上腺类固醇的合成没有明显影响。 -
Aromatase inhibitor
Fulvestrant 是一种雌激素受体拮抗剂,没有激动剂效应,其作用机制包括降调和降解雌激素受体。- Yuanqin Zhang, .et al. , Cancers (Basel), 2023, Dec 2;15(23):5691 PMID: 38067394
- Samy A. F. Morad, .et al. , Biochem Pharmacol, 2017, Apr 15; 130: 21-33 PMID: 28189725
- Kaneyasu Nishimura, .et al. , Stem Cell Reports, 2016, Apr 12; 6(4): 511-524 PMID: 26997644
- Alejandro S. Cazzulino, .et al. , Hippocampus, 2016, Jun; 26(6): 752-762 PMID: 26662713
- Rie Mukai, .et al. , Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 2016, Dec 1;311(6):R1022-R1031 PMID: 27629889
- Sakanashi M, .et al. , Circ J. , 2013, 77(7):1827-37. PMID: 23615023
-
Aromatase inhibitor
Letrozole 是一种芳香酶抑制剂。CGS 20267 是一种新型非甾体化合物,能够在体外(IC50 为 11.5 nM)和体内(ED50 为 1-3 微克/千克,口服)强效抑制芳香酶。- WEI LIU, .et al. , Exp Ther Med, 2015, Oct; 10(4): 1297-1302 PMID: 26622481
-
Aromatase inhibitor
Fadrozole 是一种非甾体类芳香化酶抑制剂,在体内对芳香化酶系统显示出非常强大且选择性的抑制作用,并在体内抑制雌激素的生物合成。- Steve U. Ayobahan, .et al. , Sci Rep, 2019, 9, Article number: 6599 PMID: 31036921
- Muth-Köhne E, .et al. , Aquat Toxicol, 2016, Jul;176:116-27 PMID: 27130971
- Ma YN, .et al. , Aquat Toxicol, 2016, Oct;179:55-64 PMID: 27571716
-
aromatase inhibitor
Alpha-Naphthoflavone 是一种合成黄酮类化合物,作为一种强效且具有竞争性的芳香化酶抑制剂,其 IC50 和 Ki 分别为 0.5 和 0.2 微摩尔。 -
Aromatase inhibitor
Fadrozole hydrochloride 是一种强效、选择性且非甾体的芳香化酶抑制剂,其 IC50 为 6.4 nM。
Endocrinology-Hormones
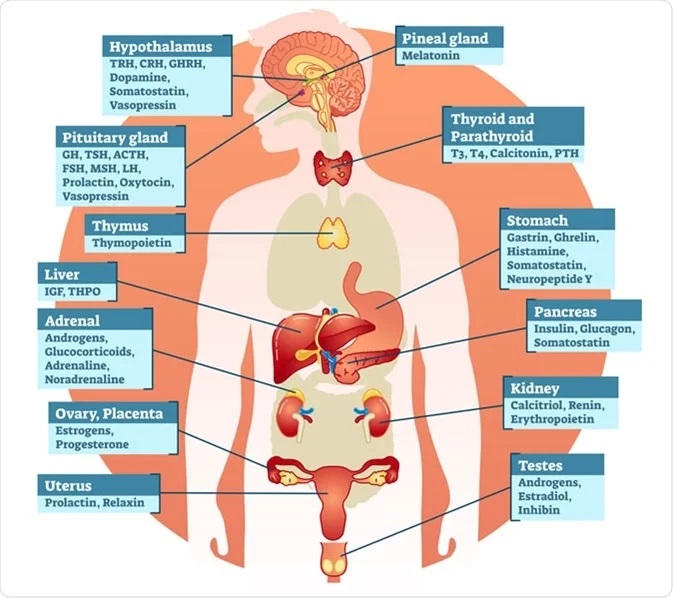

Small molecules play a pivotal role in Endocrinology Research. These are low molecular weight compounds that have a significant impact on the endocrine system, hormones, and their receptors. Here are some key aspects of how small molecules are involved in this field:
- Hormone Mimetics and Inhibitors: Small molecules are used to develop synthetic compounds that mimic the actions of hormones or inhibit their effects. For example, drugs like metformin for diabetes management and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) for breast cancer treatment are used to either mimic or block hormonal activity.
- Receptor Modulation: Small molecules can bind to hormone receptors and modulate their activity. This is crucial in developing drugs that target specific hormone receptors, like the use of small molecule agonists and antagonists to regulate thyroid hormone receptors.
- Metabolism Regulation: Endocrinology research often focuses on metabolism and how hormones like insulin regulate it. Small molecules are employed to understand and develop drugs targeting enzymes involved in metabolism, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists for diabetes treatment.
- Steroid Hormone Production: Small molecules may be utilized to influence the production of steroid hormones in the adrenal glands or gonads. This is essential for conditions like Cushing's syndrome or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Hormone Assays: In laboratory research, small molecules are used as tracers or markers in hormone assays. For instance, small molecule fluorophores can be attached to antibodies to detect hormone levels in blood samples.
Drug Development: Endocrinology research relies on small molecules as potential drug candidates. Researchers design and test small molecules for their effectiveness in modulating hormonal pathways, with the goal of developing new therapies for endocrine disorders.
In summary, small molecules are indispensable tools in Endocrinology Research, enabling scientists to better understand the endocrine system's intricacies and develop novel treatments for a wide range of hormonal disorders and conditions. Their versatility and specificity make them valuable assets in advancing our knowledge of endocrinology and improving patient care.
Endocrinology Disease Products
Endocrinology Research Products
Kisspeptin Receptor
Leptin Receptors
Melanocortin (MC) Receptors
Mineralocorticoid Receptors
Galanin Receptors
TRH Receptors
Ghrelin Receptors
Natriuretic Peptide Receptors
NPY Receptors
Motilin Receptor
PTH Receptor



