Epigenetics
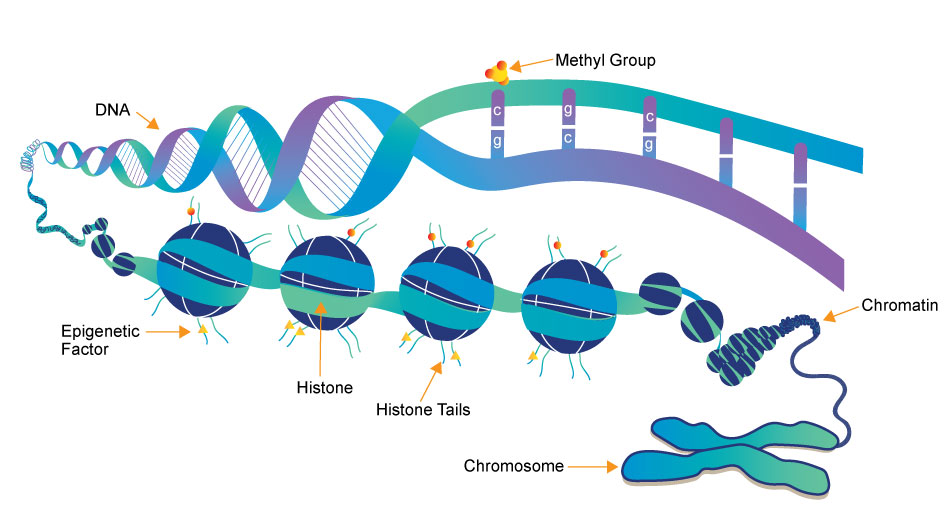

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
PARP 抑制剂
Olaparib (AZD2281) 是一种抑制剂,针对的是参与 DNA 修复的酶——聚ADP核糖聚合酶(PARP)。- Yuki Yoshino, .et al. , Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2025, Jan:742:151153 PMID: 39672008
- Saptarshi Sinha, .et al. , Med Oncol, 2024, Jan 6;41(2):49 PMID: 38184505
- Erika Nakatsuka, .et al. , Transl Oncol, 2024, Sep 12:50:102119 PMID: 39270525
- Callum G Jones, .et al. , Cancers (Basel), 2024, Feb 21;16(5):863 PMID: 38473223
- Aurelie Vanderlinden, .et al. , Br J Cancer, 2023, Nov;129(11):1829-1840 PMID: 37777579
- Saptarshi Sinha, .et al. , Exp Cell Res, 2022, Nov 1;420(1):113338 PMID: 36075449
- Subhajit Chatterjee, .et al. , J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2022, Dec;148(12):3521-3535 PMID: 35962813
- Yuki Uchihara, .et al. , Mol Cell, 2022, Jul 21;82(14):2557-2570 PMID: 35594857
- Ji-Ye Kim, .et al. , Cell Death Dis, 2022, Mar 15;13(3):239 PMID: 35293383
- Emad Matanes, .et al. , Front Oncol, 2021, Oct 27;11:745981 PMID: 34778062
- Shino Endo, .et al. , Cancer Res Commun, 2021, 1(2): 90-105
- Yan Baglo, .et al. , Transl Oncol, 2021, Nov;14(11):101198 PMID: 34418731
- Joseph M Gozgit, .et al. , Cancer cell, 2021, Jul 22;S1535-6108(21)00340-8 PMID: 34375612
- Sefinew Molla, .et al. , DNA Repair (Amst), 2021, Jun 10;105:103157 PMID: 34144488
- Jianming Wang, .et al. , Cell Rep, 2021, Feb 16;34(7):108759 PMID: 33596418
- Ai Ito, .et al. , Biogerontology, 2021, Feb;22(1):119-131 PMID: 33216250
- Tim J Wigle, .et al. , Cell Chem Biol, 2020, Jul 16;27(7):877-887 PMID: 32679093
- Ali Divan, .et al. , Pharmacol Res Perspect, 2020, Apr; 8(2): e00586 PMID: 32342655
- Jianwei Dou, .et al. , J Sep Sci, 2020, Dec 4 PMID: 33275824
- Sai Dimple Manavitha Gullipalli, .et al. , Int. J. Adv. Pharm. Biotech, 2020, 6(2) 01-08
- Chao Zhang, .et al. , J Atheroscler Thromb, 2020, Sep 25 PMID: 32981917
- Wigle TJ, .et al. , SLAS Discov, 2019, Dec 19:2472555219883623 PMID: 31855104
- Wang Q, .et al. , Cancer Med, 2019, Dec 21 PMID: 31863638
- Molla S, .et al. , Pathol Oncol Res, 2019, Nov 25 PMID: 31768967
- Alvin Z.Lu, .et al. , Biochem Pharmacol, 2019, May 7. pii: S0006-2952(19)30171-6 PMID: 31075269
- Bian C, .et al. , Nat Commun, 2019, Feb 11;10(1):693 PMID: 30741937
- HC de Silva, .et al. , Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019, 1-16 PMID: 30725116
- Kamada Y, .et al. , Fitoterapia, 2018, Sep;129:94-101 PMID: 29928967
- 2018, .et al. , FEBS Open Bio, 2018, Jun; 8(6): 1001-1012 PMID: 29928579
- Hirosumi Tamura, .et al. , Oncol Rep, 2018, Aug; 40(2): 635-646 PMID: 29917168
- Hiro Sato, .et al. , Nat Commun, 2017, 8: 1751 PMID: 29170499
- Charles-André Philip, .et al. , BMC Cancer, 2017, 17: 638 PMID: 28886696
- Rulina AV, .et al. , Cell Death Dis, 2016, Dec 1;7(12):e2505 PMID: 27906189
-
Aurora A Kinase 抑制剂
MLN8237(Alisertib)是一种选择性的Aurora A抑制剂,在无细胞试验中的IC50为1.2 nM。它对Aurora A的选择性比Aurora B高出200倍以上。目前处于第三阶段临床试验。- Shiang-Jie Yang, .et al. , Cell Death Dis, 2024, Jan 30;15(1):103 PMID: 38291041
- Vijaya Bharti, .et al. , Cell Rep, 2022, Dec 20;41(12):111826 PMID: 36543138
- Bucko PJ, .et al. , Elife, 2019, Dec 24;8. pii: e52220 PMID: 31872801
- Kimura M, .et al. , Exp Cell Res, 2018, Jun 1;367(1):73-80 PMID: 29571950
- Jing Wang, .et al. , J Cell Sci, 2017, Mar 15; 130(6): 1078-1093 PMID: 28167680
- Lessing D, .et al. , Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2016, Dec 13;113(50):14366-14371 PMID: 28182563
- Jennifer M. Sahni, .et al. , J Biol Chem, 2016, Nov 4; 291(45): 23756-23768 PMID: 27650498
-
PARP 抑制剂
ABT-888(Veliparib) 是一种潜在的抗癌药物,作为 PARP 抑制剂 发挥作用。- Subhajit Chatterjee, .et al. , Cell Signal, 2021, Apr;80:109902 PMID: 33373686
-
PARP 抑制剂
AG-014699(Rucaparib)是一种PARP抑制剂,它抑制多聚(ADP-核糖)聚合酶(PARP),这是DNA修复中的关键酶。- Ali Divan, .et al. , Pharmacol Res Perspect, 2020, Apr; 8(2): e00586 PMID: 32342655
- Tahira Baloch, .et al. , BMC Cancer, 2019, Jan 10;19(1):44 PMID: 30630446
-
PARP1 抑制剂
AG14361 是一种强效的 PARP 抑制剂,在 MMR(错配修复) -完好/缺陷细胞中增强了 TMZ 的细胞毒性。- Vimal Pandey, .et al. , Scientific Reports, 2019, 9, Article number: 5012 PMID: 30899038
-
EGFR 抑制剂
AG 490 是一种选择性的 EGF 受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(EGFR 和 ErbB2 的 IC50 值分别为 2 和 13.5 μM)。同时抑制 JAK2,对 Lck、Lyn、Btk、Syk 和 Src 无活性。- Matozaki M, .et al. , Exp Cell Res, 2019, Feb 15. pii: S0014-4827(18)31030-9 PMID: 30776355
-
Aurora A 抑制剂
Aurora A Inhibitor I 是一种强效且选择性的 Aurora A 激酶 (AurA) 抑制剂,其 IC50 值为 3.4 nM(针对 Aurora A),并且对 Aurora B 具有极高的选择性,高达 1000 倍;这是一种有用的工具化合物,用于研究 Aurora A 激酶 在细胞中的作用。 -
JAK2 抑制剂
AZ-960 是一种强效、选择性和与ATP竞争的 JAK2抑制剂,在体外对 JAK2激酶 的抑制常数(Ki)为0.45 nM,并且能在成人T细胞白血病(ATL)细胞中诱导生长停滞和凋亡。- Rongshou Wu, .et al. , Sci Rep, 2023, 13: 16998 PMID: 37813900
-
Aurora Kinase B 抑制剂
AZD 1152-HQPA 是一种高效且选择性的 Aurora B 抑制剂,其 Ki 值分别为 0.36 nM(Aurora B)和 1369 nM(Aurora A),并且相对于其他50种激酶具有高度的特异性。- Sakamoto K, .et al. , Leukemia, 2018, May 23 PMID: 29795241
- Jennifer M. Sahni, .et al. , J Biol Chem, 2016, Nov 4; 291(45): 23756-23768 PMID: 27650498
-
JAK1/JAK2 抑制剂
AZD1480 是一种新型的强效小分子 JAK2 抑制剂,其 IC50 为 0.26 nM。- Simona Moravcova, .et al. , Life (Basel), 2021, Oct 18;11(10):1105 PMID: 34685476
-
HDAC 抑制剂
Belinostat (PXD101) 是一种 HDAC 抑制剂,在 HeLa 细胞提取物中抑制 HDAC 活性,其 IC50 为 27 nM。- Shariful Islam, .et al. , Blood Adv, 2020, 4(20): 5297-5310 PMID: 33108458
-
PARP1 抑制剂
BSI-201 是一种强效的 PARP-1 抑制剂,并已显示能够穿越 血脑屏障。- Jianwei Dou, .et al. , J Sep Sci, 2020, Dec 4 PMID: 33275824
-
Topoisomerase I 抑制剂
Camptothecin 是一种具有细胞毒性的喹啉生物碱,它抑制 DNA 酶 拓扑异构酶 I(topo I)。- Kengo Takeda, .et al. , Int J Mol Sci, 2024, Mar 26;25(7):3693 PMID: 38612503
-
JAK3 抑制剂
CP-690550(柠檬酸托法替尼)是一种口服可用的、高度选择性的Janus激酶(JAK)家族酶的抑制剂。- Fujita KI, .et al. , J Pharm Sci, 2017, Sep;106(9):2632-2641 PMID: 28479358
-
JAK 抑制剂
CYT387 是一种抑制剂,针对 Janus kinases JAK1 和 JAK2,作为 ATP 竞争剂,其 IC50 值分别为 11 nM 和 18 nM。- Bopei Cui, .et al. , Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, Sep 25;8(1):366 PMID: 37743418
- Alex Bainbridge, .et al. , Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, April
-
DNA Methyltransferase 抑制剂s
Decitabine 是一种去甲基化剂。它通过抑制 DNA 甲基转移酶来去甲基化 DNA。- Tianxing Ying, .et al. , Cancers (Basel), 2022, Dec 30;15(1):243 PMID: 36612238
- Borbala Szabo, .et al. , J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2022, Sep 5;dgac496 PMID: 36059148
- Sangni Qian, .et al. , Clin Epigenetics, 2022, Sep 5;14(1):111 PMID: 36064442
- Borb??la Szab??, .et al. , J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2020, Jun 1;105(6):dgaa156 PMID: 32232382
- Bracha Shraibman, .et al. , Mol Cell Proteomics, 2016, Sep; 15(9): 3058-3070 PMID: 27412690
-
HDAC 抑制剂
Droxinostat 是一种选择性的 HDAC3、HDAC6 和 HDAC8 抑制剂,对 HDAC6 和 HDAC8 的抑制作用相当,其半抑制浓度(IC50)分别为 2.47 和 1.46 微摩尔/升。 -
SIRT1 抑制剂
EX 527 是一种强效且选择性的 SIRT1 类 III 组蛋白去乙酰化酶 抑制剂,在无细胞试验中的 IC50 为 38 nM。- Yue He, .et al. , FASEB J, 2024, Oct 15;38(19):e70095 PMID: 39373984
- Qiang Chen, .et al. , J Bioenerg Biomembr, 2022, Feb;55(1):33-42 PMID: 36525212
- Flavien Bizot, .et al. , Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2022, Nov 21;30:606-620 PMID: 36514350
- Takeshi Nakamura, .et al. , Shimane Journal of Medical Science, 2022, 38 (2), 59-66
- Bugga Paramesha, .et al. , Antioxidants (Basel), 2021, Feb 24;10(3):338 PMID: 33668369
- Wenhui Yao, .et al. , J Cell Physiol, 2020, 07 August
- Guang Bai, .et al. , Epigenetics of Chronic Pain, 2019, Pages 1-48
- Yoshikawa A, .et al. , J Neurochem, 2015, Feb;132(3):342-53 PMID: 25351847
-
mTOR 抑制剂
FK-506 是一种免疫抑制药物,主要用于异体器官移植后,通过降低患者免疫系统的活性,从而减少器官排斥的风险。它通过减少 T 细胞产生的白细胞介素-2 (IL-2) 来发挥作用。- Ogawa Y, .et al. , Neurobiol Dis, 2018, Oct;118:142-154 PMID: 30026035
- Yuko Okamoto, .et al. , J Drug Deliv Sci Technol, 2018, 47: 62-66
-
Aurora B Kinase 抑制剂
Hesperadin 是一种针对人类 Aurora B 的抑制剂,其 IC50 值为 40 nM,用于防止底物的磷酸化。它显著降低了 AMPK、Lck、MKK1、MAPKAP-K1、CHK1 和 PHK 的活性,但在体内不抑制 MKK1 的活性。- Wenbin Ji, .et al. , PLoS One, 2016, 11(4): e0153518 PMID: 27082996
-
PARP 抑制剂
3-氨基苯甲酰胺是一种新型的 PARP 抑制剂,已知通过抑制 DNA 损伤的修复,能够在体外使细胞对辐射敏感化。- Kamada Y, .et al. , Fitoterapia, 2018, Sep;129:94-101 PMID: 29928967
-
HDAC 抑制剂
ITF2357(Givinostat)是一种 HDACs 抑制剂,具有潜在的 抗炎、抗血管生成 和 抗肿瘤 活性。- Flavien Bizot, .et al. , Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2022, Nov 21;30:606-620 PMID: 36514350
-
HDAC 抑制剂
JNJ-26481585(Quisinostat)是一种全面的HDAC抑制剂,对HDAC1具有显著的效力(IC(50),0.16 nmol/L)。- Minoru Ueda, .et al. , Plant Physiol, 2017, Dec; 175(4): 1760-1773 PMID: 29018096
-
CDK/Aurora A/B 抑制剂
JNJ-7706621 是一种广谱 CDK 抑制剂,在 CDK1/2 上具有最高的抑制活性,其 IC50 分别为 9 nM/4 nM,并且在无细胞试验中对 CDK1/2 的选择性比 CDK3/4/6 高出6倍以上。它还强效抑制 Aurora A/B,并且对 Plk1 和 Wee1 无活性。- Yuta Tanizaki, .et al. , Commun Biol, 2022, 5: 112 PMID: 35132135
-
HDAC 抑制剂
LAQ824(NVP-LAQ824)是一种强效的新型组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂,对多发性骨髓瘤具有显著的活性。- De-Run Chen, .et al. , Appl Mater Today, 2022, 26: 101363
-
HDAC 抑制剂
LBH589 是一种羟胺酸,作为非选择性 HDAC 抑制剂,其对 HDAC1 的 IC50 为 0.23 nM。- Jalila Chagraoui, .et al. , Cell Stem Cell, 2021, Jan 7;28(1):48-62.e6 PMID: 33417871
- Gils Jose, .et al. , Cancers (Basel), 2020, Oct 31;12(11):E3211 PMID: 33142721
- Shariful Islam, .et al. , Blood Adv, 2020, 4(20): 5297-5310 PMID: 33108458
- Giovanni Bocci, .et al. , ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci, 2020, Oct 14
- Justin Kale, .et al. , EMBO Rep, 2018, Sep; 19(9): e45235 PMID: 29987135
-
JAK 抑制剂
LY2784544 被确认为对 JAK2-V617F 具有高度选择性,并已进入人类临床试验阶段,用于治疗多种骨髓增生性疾病。 -
HDAC 抑制剂
MC1568 是 HDAC 抑制剂的一种,它通过改变细胞周期中大多数处于 G1 阶段的各种重要基因的遗传表达,抑制组蛋白去乙酰化酶 II 类,从而导致乳腺癌细胞通过凋亡死亡。- Bopei Cui, .et al. , Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, Sep 25;8(1):366 PMID: 37743418
- Vivek Bora, .et al. , Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 2021, 6 October
- Minoru Ueda, .et al. , Plant Physiol, 2017, Dec; 175(4): 1760-1773 PMID: 29018096
- S Ishikawa, .et al. , Int J Cancer., 2014, 135(11): 2528-2536 PMID: 24346863
- Usui T, .et al. , Hypertension., 2014, Feb;63(2):397-403 PMID: 24166750
-
HDAC 抑制剂
MGCD0103(Mocetinostat)是一种苯甲酰胺类组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂,主要通过抑制组蛋白去乙酰化酶1(HDAC1),同时也能抑制HDAC2、HDAC3和HDAC11。- Mari Ishigami-Yuasa, .et al. , Biol Pharm Bull, 2019, 42, 448-452 PMID: 30828077
- Guang Bai, .et al. , Epigenetics of Chronic Pain, 2019, Pages 1-48
-
HDAC 抑制剂
MS-275(Entinostat)是一种强效的HDAC抑制剂,其IC50分别为HDAC1的0.3uM和HDAC3的8uM。- Wenguang Liu, .et al. , Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2024, Dec 20:739:150970 PMID: 39550862
- Vivek Bora, .et al. , Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 2021, 6 October
- Taito Kashio, .et al. , Tissue Barriers, 2021, May 6;1911195 PMID: 33955828
- Ting-Yu Chang, .et al. , Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, Jun;138:111485 PMID: 33740521
- Arshdeep Singh, .et al. , Eur J Med Chem, 2021, Apr 5;215:113169 PMID: 33588178
- Minoru Ueda, .et al. , Plant Physiol, 2017, Dec; 175(4): 1760-1773 PMID: 29018096
- Parthenolide((-)-Parthenolide)是一种天然存在于小白菊(Tanacetum parthenium)中的倍半萜内酯。
-
HDAC 抑制剂
PCI-24781 是一种广谱的苯基羟胺酸 HDAC 抑制剂。- Kazuya Tsumagari, .et al. , Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2021, Jul 23;563:60-65 PMID: 34062387
-
Aurora 抑制剂
PHA-680632 是一种强效的 Aurora A、Aurora B 和 Aurora C 抑制剂,其半抑制浓度(IC50)分别为 27 nM、135 nM 和 120 nM。相比之下,它对 FGFR1、FLT3、LCK、PLK1、STLK2 和 VEGFR2/3 的 IC50 高出 10 到 200 倍。 -
Aurora 抑制剂
Danusertib (PHA-739358) 是一种针对 Aurora A/B/C 的 Aurora 激酶抑制剂,在无细胞试验中的 IC50 分别为 13 nM/79 nM/61 nM,对 Abl、TrkA、c-RET 和 FGFR1 有适度的抑制效力,对 Lck、VEGFR2/3、c-Kit、CDK2 等的抑制效力较低。目前处于临床试验第二阶段。- Vijaya Bharti, .et al. , Cell Rep, 2022, Dec 20;41(12):111826 PMID: 36543138
-
HDAC 抑制剂
Pyroxamide (NSC 696085) 是一种强效的 HDAC1 亲和纯化抑制剂,并且在与该药剂共培养的 MEL 细胞中导致乙酰化核心组蛋白的积累。 -
HDAC 抑制剂
SB939 是一种口服 HDAC 抑制剂,选择性针对 I 类、II 类和 IV 类 HDAC,并在体外 HDAC1 活性测定中显示出 77 nM 的 IC50 值。- Giovanni Bocci, .et al. , ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci, 2020, Oct 14
-
PIM1 抑制剂
SGI-1776 free base 是一种新型的 ATP 竞争性抑制剂,针对 Pim1,其在无细胞测定中的 IC50 为 7 nM,相对于 Pim2 和 Pim3 分别具有 50 倍和 10 倍的选择性,同时对 Flt3 和 haspin 也具有强效。目前处于第一阶段临床试验。- Ishikawa C, .et al. , Eur J Haematol, 2017, Dec;99(6):495-504 PMID: 28833639
-
Aurora 抑制剂
SNS-314 Mesylate 是一种强效且选择性的 Aurora A、Aurora B 和 Aurora C 抑制剂,其半抑制浓度(IC50)分别为 9 nM、31 nM 和 3 nM。相比之下,它对 Trk A/B、Flt4、Fms、Axl、c-Raf 和 DDR2 的抑制作用较弱。目前处于临床试验第一阶段。 -
HDAC 抑制剂
钠丁酸(NaB,丁酸钠盐),即丁酸的钠盐,是一种组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂,能与I类和II类组蛋白去乙酰化酶(HDACs)的锌位点竞争性结合。




