Epigenetics - PARP1
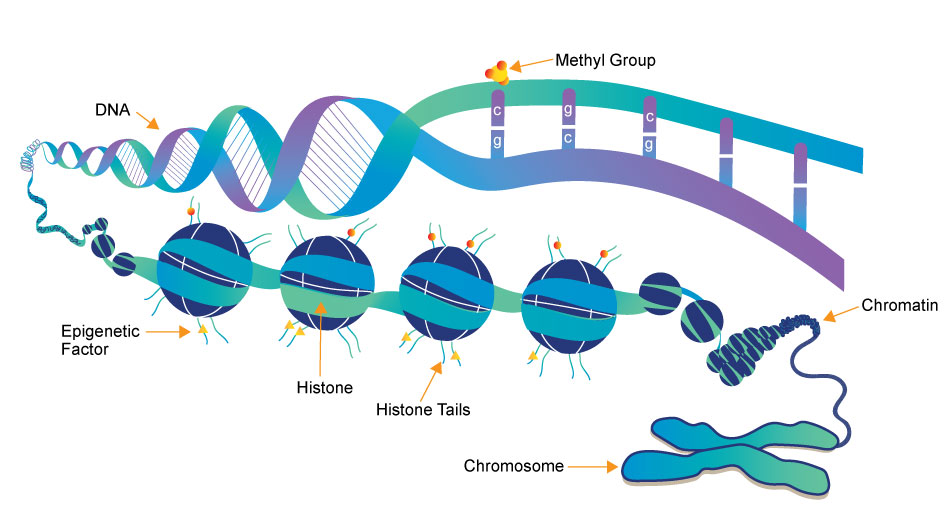

Epigenetics research delves into the molecular mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular traits without altering the underlying DNA sequence. One crucial aspect of this field is the role of small molecules, which act as powerful regulators of epigenetic modifications. These small compounds, typically comprising a few dozen to a few hundred atoms, have emerged as essential tools in understanding and manipulating the epigenome.
- DNA Methylation Inhibitors: Small molecules like 5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine are DNA methyltransferase inhibitors. They block the addition of methyl groups to DNA, leading to DNA demethylation. This can reactivate silenced genes, potentially offering therapeutic avenues for conditions like cancer.
- HDAC inhibitors: HDACs remove acetyl groups from histone proteins, contributing to gene repression. Small molecule HDAC inhibitors, such as Vorinostat and Romidepsin, can reverse this process by increasing histone acetylation, allowing genes to be more accessible for transcription. These inhibitors are being explored for cancer therapy and other conditions.
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors: Small molecules like GSK126 inhibit specific histone methyltransferases, affecting histone methylation patterns. This can alter gene expression, making them promising candidates for cancer and other diseases with epigenetic dysregulation.
- RNA Modulators: Small molecules can also target non-coding RNAs involved in epigenetic regulation. For instance, small molecules called small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can be designed to target and degrade specific long non-coding RNAs, influencing gene expression.
- Epigenetic Reader Domain Inhibitors: These small molecules target proteins that recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks. Examples include inhibitors of bromodomain-containing proteins (BET inhibitors), which can disrupt gene regulation by interfering with protein-DNA interactions.
Small molecules in epigenetics research not only provide insights into the fundamental biology of gene regulation but also hold immense promise for developing novel therapeutics. Their ability to selectively modulate specific epigenetic marks and pathways has led to ongoing clinical trials and drug development efforts for various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Understanding and harnessing the power of these small molecules is at the forefront of modern epigenetics research, offering new hope for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
3 key components involved in the regulation of epigenetic modifications
Epigenetics Writer
Epigenetics writers are enzymes responsible for adding chemical marks or modifications to DNA or histone proteins. These marks include DNA methylation (addition of methyl groups to DNA) and histone modifications (such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.).
Epigenetics Reader
Function: Epigenetics readers are proteins that can recognize and bind to specific epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. These reader proteins interpret the epigenetic code and facilitate downstream cellular processes, such as gene activation or repression.
Epigenetics Eraser
Function: Epigenetics erasers are enzymes responsible for removing or reversing epigenetic marks on DNA or histones. This process allows for the dynamic regulation of gene expression and the resetting of epigenetic states during various stages of development and in response to environmental changes.
-
PARP 抑制剂
Olaparib (AZD2281) 是一种抑制剂,针对的是参与 DNA 修复的酶——聚ADP核糖聚合酶(PARP)。- Yuki Yoshino, .et al. , Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2025, Jan:742:151153 PMID: 39672008
- Saptarshi Sinha, .et al. , Med Oncol, 2024, Jan 6;41(2):49 PMID: 38184505
- Erika Nakatsuka, .et al. , Transl Oncol, 2024, Sep 12:50:102119 PMID: 39270525
- Callum G Jones, .et al. , Cancers (Basel), 2024, Feb 21;16(5):863 PMID: 38473223
- Aurelie Vanderlinden, .et al. , Br J Cancer, 2023, Nov;129(11):1829-1840 PMID: 37777579
- Saptarshi Sinha, .et al. , Exp Cell Res, 2022, Nov 1;420(1):113338 PMID: 36075449
- Subhajit Chatterjee, .et al. , J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2022, Dec;148(12):3521-3535 PMID: 35962813
- Yuki Uchihara, .et al. , Mol Cell, 2022, Jul 21;82(14):2557-2570 PMID: 35594857
- Ji-Ye Kim, .et al. , Cell Death Dis, 2022, Mar 15;13(3):239 PMID: 35293383
- Emad Matanes, .et al. , Front Oncol, 2021, Oct 27;11:745981 PMID: 34778062
- Shino Endo, .et al. , Cancer Res Commun, 2021, 1(2): 90-105
- Yan Baglo, .et al. , Transl Oncol, 2021, Nov;14(11):101198 PMID: 34418731
- Joseph M Gozgit, .et al. , Cancer cell, 2021, Jul 22;S1535-6108(21)00340-8 PMID: 34375612
- Sefinew Molla, .et al. , DNA Repair (Amst), 2021, Jun 10;105:103157 PMID: 34144488
- Jianming Wang, .et al. , Cell Rep, 2021, Feb 16;34(7):108759 PMID: 33596418
- Ai Ito, .et al. , Biogerontology, 2021, Feb;22(1):119-131 PMID: 33216250
- Tim J Wigle, .et al. , Cell Chem Biol, 2020, Jul 16;27(7):877-887 PMID: 32679093
- Ali Divan, .et al. , Pharmacol Res Perspect, 2020, Apr; 8(2): e00586 PMID: 32342655
- Jianwei Dou, .et al. , J Sep Sci, 2020, Dec 4 PMID: 33275824
- Sai Dimple Manavitha Gullipalli, .et al. , Int. J. Adv. Pharm. Biotech, 2020, 6(2) 01-08
- Chao Zhang, .et al. , J Atheroscler Thromb, 2020, Sep 25 PMID: 32981917
- Wigle TJ, .et al. , SLAS Discov, 2019, Dec 19:2472555219883623 PMID: 31855104
- Wang Q, .et al. , Cancer Med, 2019, Dec 21 PMID: 31863638
- Molla S, .et al. , Pathol Oncol Res, 2019, Nov 25 PMID: 31768967
- Alvin Z.Lu, .et al. , Biochem Pharmacol, 2019, May 7. pii: S0006-2952(19)30171-6 PMID: 31075269
- Bian C, .et al. , Nat Commun, 2019, Feb 11;10(1):693 PMID: 30741937
- HC de Silva, .et al. , Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019, 1-16 PMID: 30725116
- Kamada Y, .et al. , Fitoterapia, 2018, Sep;129:94-101 PMID: 29928967
- 2018, .et al. , FEBS Open Bio, 2018, Jun; 8(6): 1001-1012 PMID: 29928579
- Hirosumi Tamura, .et al. , Oncol Rep, 2018, Aug; 40(2): 635-646 PMID: 29917168
- Hiro Sato, .et al. , Nat Commun, 2017, 8: 1751 PMID: 29170499
- Charles-André Philip, .et al. , BMC Cancer, 2017, 17: 638 PMID: 28886696
- Rulina AV, .et al. , Cell Death Dis, 2016, Dec 1;7(12):e2505 PMID: 27906189
-
PARP 抑制剂
AG-014699(Rucaparib)是一种PARP抑制剂,它抑制多聚(ADP-核糖)聚合酶(PARP),这是DNA修复中的关键酶。- Ali Divan, .et al. , Pharmacol Res Perspect, 2020, Apr; 8(2): e00586 PMID: 32342655
- Tahira Baloch, .et al. , BMC Cancer, 2019, Jan 10;19(1):44 PMID: 30630446
-
PARP1 抑制剂
AG14361 是一种强效的 PARP 抑制剂,在 MMR(错配修复) -完好/缺陷细胞中增强了 TMZ 的细胞毒性。- Vimal Pandey, .et al. , Scientific Reports, 2019, 9, Article number: 5012 PMID: 30899038
-
PARP1 抑制剂
BSI-201 是一种强效的 PARP-1 抑制剂,并已显示能够穿越 血脑屏障。- Jianwei Dou, .et al. , J Sep Sci, 2020, Dec 4 PMID: 33275824
-
PARP 抑制剂
MK-4827 是一种新型的、高效的、口服生物利用度高的 PARP-1 和 PARP-2 抑制剂。- Joseph M Gozgit, .et al. , Cancer cell, 2021, Jul 22;S1535-6108(21)00340-8 PMID: 34375612
- Ann-Katrin Hopp, .et al. , Molecular cell, 2021, Jan 21; 81(2): 340–354 PMID: 33450210
- Bian C, .et al. , Nat Commun, 2019, Feb 11;10(1):693 PMID: 30741937
- Tahira Baloch, .et al. , BMC Cancer, 2019, Jan 10;19(1):44 PMID: 30630446
- Khalid Hilmi, .et al. , Sci Adv, 2017, May; 3(5): e1601898 PMID: 28560323
-
PARP 抑制剂
BMN-673 是一种口服生物利用度的抑制剂,针对核酶多聚(ADP-核糖)聚合酶(PARP)具有潜在的抗肿瘤活性。- Subhajit Chatterjee, .et al. , J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2022, Dec;148(12):3521-3535 PMID: 35962813
- Charles-André Philip, .et al. , BMC Cancer, 2017, 17: 638 PMID: 28886696
-
PARP 抑制剂
PJ 34 盐酸盐是一种强效的聚(ADP-核糖)聚合酶(PARP)抑制剂(EC50 = 20 nM)。- Wigle TJ, .et al. , SLAS Discov, 2019, Dec 19:2472555219883623 PMID: 31855104
- Alvin Z.Lu, .et al. , Biochem Pharmacol, 2019, May 7. pii: S0006-2952(19)30171-6 PMID: 31075269
-
PARP-1 抑制剂
Rucaparib 是一种强效的纯化全长人类 PARP-1 抑制剂,并且在 LoVo 和 SW620 细胞中显示出更高的细胞 PARP 抑制作用。- Jianwei Dou, .et al. , J Sep Sci, 2020, Dec 4 PMID: 33275824
-
PARP 抑制剂
BMN-673 (8R,9S) 是 BMN-673 的 (8R,9S) 对映体。BMN 673 是一种新型的 PARP 抑制剂,其 IC50 为 0.58 nM。 -
PARP 抑制剂
PJ34 是一种新型的高效特异性 PARP-1/2 抑制剂,其 EC50 为 20 nM。- Tim J Wigle, .et al. , Cell Chem Biol, 2020, Jul 16;27(7):877-887 PMID: 32679093
-
PARP1/PARP2 抑制剂
Niraparib tosylate (MK-4827 tosylate) 是一种高效且可口服吸收的 PARP1 和 PARP2 抑制剂,其 IC50 分别为 3.8 nM 和 2.1 nM。- Laurie B Schenkel, .et al. , Cell Chem Biol, 2021, Mar 2;S2451-9456(21)00095-7 PMID: 33705687
-
PARP 抑制剂
Rucaparib Camsylate 是一种 PARP 抑制剂,其对 PARP1 的 Ki 值为 1.4 nM,并且还显示出对其他八个 PARP 域的结合亲和力。 -
PARP1 and PARP2 抑制剂
Niraparib hydrochloride (MK-4827 hydrochloride) 是一种高效且可口服吸收的 PARP1 和 PARP2 抑制剂,其 IC50 分别为 3.8 nM 和 2.1 nM。 -
Tankyrase 抑制剂
Tankyrase-IN-2(化合物5k)是一种高效、选择性且可口服活性的tankyrase抑制剂(分别对TNKS1、TNKS2以及PARP1的IC50为10、7和710 nM)。 -
PARP1/2 抑制剂
Talazoparib tosylate (BMN 673ts) 是一种新型、高效且可口服的 PARP1/2 抑制剂,其对 PARP1 的 IC50 为 0.57 nM。- Majid Momeny, .et al. , EMBO Mol Med, 2024, Jun 17 PMID: 38886591
-
PARP 抑制剂
Veliparib dihydrochloride 是一种强效的 PARP 抑制剂,分别以 Kis 值 5.2 和 2.9 nM 抑制 PARP1 和 PARP2。 -
PARP1/PARP2 抑制剂
E7449 是一种强效的 PARP1 和 PARP2 抑制剂,同时也能抑制 TNKS1 和 TNKS2,其半抑制浓度(IC50)分别为 PARP1 2.0 nM、PARP2 1.0 nM、TNKS1 和 TNKS2 约50 nM,使用的底物为 32P-NAD+。 -
PARP1 抑制剂
Niraparib R-enantiomer (MK-4827 R-enantiomer) 是一种优秀的 PARP1 抑制剂,其 IC50 为 2.4 nM。




